 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...Products
- Heating and Cooling
- Outdoor Living & Patio
- Solar Kits
- Solar Products
- Solar Panels
- Solar Panel Kits
- Solar Generators
- Inverters
- Inverter Monitoring
- Inverter Accessories
- Balance of Systems
- Racking and Mounting
- Rails
- Flashings
- Splice Kits
- Stopper Sleeves
- Conduit Mounts
- Attachments
- Brace Assembly
- Base Mount
- Brackets
- Bolts
- Clamps
- Caps
- L-Feet
- Washers
- Skirt
- Lugs
- Tilt Legs
- Hooks
- Stand-Offs
- Ballast Bay
- Top of Pole Mount
- Side of Pole Mount
- Flush Mount Kits
- Ground Mount Kits
- Roof Mount Kits
- Hardware Packages
- Wire Management
- Batteries
- Battery Accessories
- Charge Controllers
- Tools and Supplies
- View All Products
Solar Components
Solar Components

| Solar Power System Components Overview |
|
Understanding the products or components that enable a solar energy system to function properly is important. Any potential solar power system owner should take the time to understand what summarizes a photovoltaic array and how those components work to enable electrical generation for the energy needs. |
| Solar Energy System |
|
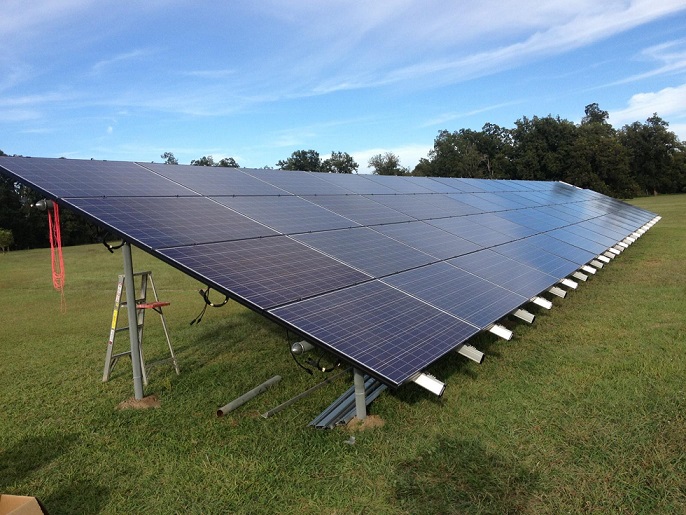
A Solar Energy System is a renewable energy generating system that collects photovoltaic energy from the sun and converts it into usable electricity. Often found as roof-top PV arrays, these systems can range in size and are able to power different types of properties - such as residential, commercial, and utility-scale zones. Photovoltaic systems can be used in multiple applications: standard arrays such as roof-top or ground mount serve to generate energy for a residence or building, while other non-traditional systems can be utilized to power other objects or function (such as space satellites, hand-held calculators or vehicles). Standard residential or commercial solar power systems consist of a core set of components - (Solar Panels, Inverters, DC/AC Disconnects, Meters, Wiring, Racking and Mounting), these are usually grid-tied. Some systems require additional components added to the core set to function – (Charge Controllers, Batteries, Additional Balance of Systems items and more), these are usually off-grid. |
| Solar Panels | |
|
Solar Panels or PV modules are the most commonly known component in a photovoltaic array. Made up of mostly solar cells, framing, and glass; solar panels work by collecting and harnessing photovoltaic energy from the sun, and delivering that energy as ‘direct current’ (DC) power to an inverter or converter component (may be a charge controller in some instances). |
 |
|
The DC power generated by a solar module is an electric current that flows in a constant direction. This type of power is generally not readily useable for standard electric demands, and must be translated into ‘alternating current’ (AC) power before it can be used for standard electric devices inside a home or building. |
|
| Inverters | |
| Inverters (or Converters) intake DC power generated by a solar panel and process that energy by converting it into AC power, the resulting power can then be sent to a breaker or balance of system component and is available for standard use. Inverters may be located after a charge controller and battery bank in certain off-grid energy systems. |  |
|
Inverters come in different types of sizes and use various technologies to enable efficiency in the function to produce AC power. The most common inverters are; String Inverters, Central Inverters, Microinverters, and Battery-based Inverters. Each will carry different mechanical and technical characteristics. |
|
| Monitoring | |
| Monitoring Equipment components are usually connected to a concurrent Inverter manufacturer, and they view and relay system energy information analytics to a in product console or web connected device through their proprietary software. Monitoring Equipment components may be integrated into an Inverter, or in some instances – be connected to another component of a photovoltaic array. |  |
|
Monitoring technology is able to display information ranging from energy generated by the solar panels, to real-time data, to immediate fault detection and troubleshooting, to energy yield data over a set amount of time. A comprehensive Monitoring system can benefit the system operator to better understand the way the solar energy system is operating, (and measures that can be taken to better increase yields, productivity, maintenance and other variables) in real time or over the course of the systems lifespan. |
|
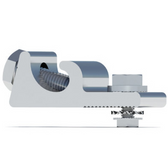
| Racking | |
| Racking and Mounting components work to ensure a PV array is connected to either the ground or a roof and is made up of multiple key products that encompass an entire racking system. |  |
|
Most racking systems will use a combination of: Rails, Flashings, Lugs, Mounting Brackets, Wire Clips, Splice Kits, Braces, End Caps, Attachments, Tilt Legs - and other components to complete a full racking and mounting system. Ground mount systems will require concrete and steel piping in addition to a complete racking kit to be placed onto land. |
|
| Balance of Systems | |
| Balance of System components work to combine other electrical products within the system, then combining and delivering a series of power control and distribution options for any PV array. |  |
|
Commonly, most items that make up Balance of Systems products include: DC/AC Disconnects, Junction Boxes, Combiner Boxes, Circuit Breakers, Fuses, Load Centers, Rapid Shutdowns, Surge Devices, among other components that may vary from system to system. These components will differ per individual solar energy system, as some systems will need more or less power control and distribution depending on their application. |
|
| Wiring | |
| Wiring acts to ensure other solar energy components are interconnected, and can pass energy from one device onto another. PV Wire is commonly used to move energy from the Solar Modules to the Inverter(s), and then be transformed to be sent for another product within the photovoltaic array supply chain. |  |
|
Wires will generally be made of aluminum or copper, be solid or standard, are insulated, and meant to either pass through DC current or AC current depending on where they are positioned and connected. Wires will also be color coded for safety and identification purposes by a system operator or inspector who needs to understand which wire controls a certain current, (Positive, Negative, Grounded, etc.) |
|
| Charge Controllers |
|
| Charge Controllers work to regulate electrical charge and they limit the rate at which electric current is added to or withdrawn from the Batteries. They work to control voltage and watts from Solar Panels; thus, passing through more stable energy, preventing overcharging and protecting against overvoltage - which can hinder and reduce Battery performance or lifespan. |  |
|
Charge Controllers come with various types of sizes and technologies that enable generally an off-grid (Battery Bank) system to function properly. These two types of technologies are MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) and PWM (Pulse Width Modulation). Charge Controllers are often used within an off-grid or hybrid with battery back-up solar energy system. |
|
| Batteries | |
| Batteries enable the ability to store solar power for use at a later date. They are used within off-grid or hybrid solar electric arrays, which require power to be used in the case of lack of available sunlight (night time), unstable power distribution from a utility company, or lack of access to a utility supplier. |  |
|
Off-grid and hybrid systems will often utilize a Battery, (or series of Batteries), to store collected energy delivered by a Charge Controller, Inverter or both – then making the resulting energy ready for withdrawal on demand when a system operator requires it. |
|
| More Solar Information | |
| Understand how solar works by visiting our Learn Solar section, or find out how to go solar by reading our Solar Guide. See all Solar Resources. |
|