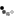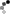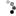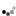 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...Products
- Solar Panels
- Solar Panel Kits
- Solar Generators
- Inverters
- Inverter Monitoring
- Inverter Accessories
- Balance of Systems
- Racking and Mounting
- Rails
- Flashings
- Splice Kits
- Stopper Sleeves
- Conduit Mounts
- Attachments
- Brace Assembly
- Base Mount
- Brackets
- Bolts
- Clamps
- Caps
- L-Feet
- Washers
- Skirt
- Lugs
- Tilt Legs
- Hooks
- Stand-Offs
- Ballast Bay
- Top of Pole Mount
- Side of Pole Mount
- Flush Mount Kits
- Ground Mount Kits
- Roof Mount Kits
- Hardware Packages
- Wire Management
- Batteries
- Battery Accessories
- Charge Controllers
- Tools and Supplies
- View All Products
Solaris Blog - Solar Advice
Solar Panel Ratings Explained
Posted by Brandi Casey on 22nd Jun 2018

When comparing solar panels, it is important to consider output wattages, total capacity and power output. The production output of solar panels varies depending on a number of factors, such as where you live (number of sun hours), ambient temperature and efficiency ratings. Here is our breakdown of what to look for, and how to compare solar modules.
*You can view detailed information and specifications on all of our products by scrolling down past the product description on each individual item in our store.
Wattage
Solar panel watts represent the panel’s expected power production under ideal sunlight and temperature conditions. Typical modules are rated between 250 to 400 watts, with higher watt modules being the preferred options. Higher watt modules not only usually have higher efficiency ratings but require less modules to achieve your ideal energy needs. The overall wattage of your system is what primarily determines the cost of your system.
*Average wattage as of June 2018
Wattage is calculated by multiplying the total volts and amps of the solar module. Module volts represent the force of the electricity generated by the panels, while amps refer to the aggregate amount of energy used. All technical data can regarding your chosen module can be found in the specifications sheet provided by the manufacturer.
Sun Hours
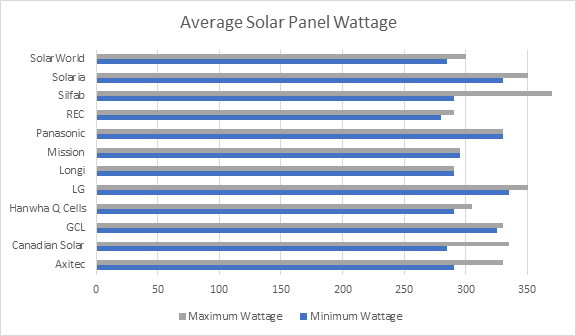
To determine how much energy your solar panel system will produce, multiply your number of sun hours based on the below map.
Zone 1 - 6 hours
Zone 2 - 5.5 hours
Zone 3 - 5 hours
Zone 4 - 4.5 hours
Zone 5 - 4.2 hours
Zone 6 - 3.5 hours
Example: California – Zone 3 – Hours 5 | 300-Watt Solar Panel
5 Hours x 300 Watts = 1,500 watts or 1.5 kilowatt-hours (kwh)
Each solar panel in your system will produce between 500-550 kWh of power per year
For those in areas with fewer sun hours such as Washington, we recommend using microinverters or optimizers. Low irradiance panels like those offered by Canadian Solar’s CS6U and CS6K series work well in low lighting situations, and on cloudy days. Checking the irradiance ratings on panels is important for any installation taking place in areas with a lot of cloudy days, those who live in sunny areas can also benefit from utilizing the modules as they will get more energy generation in the morning and evening.
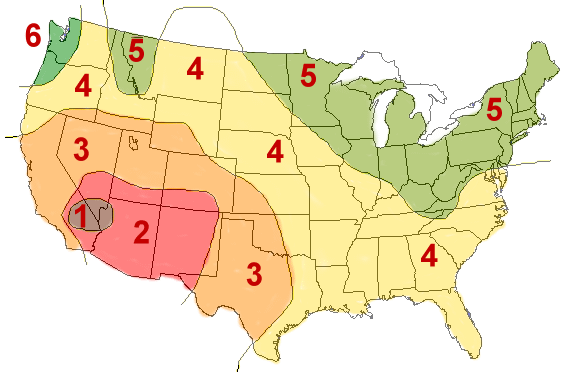
Efficiency Ratings
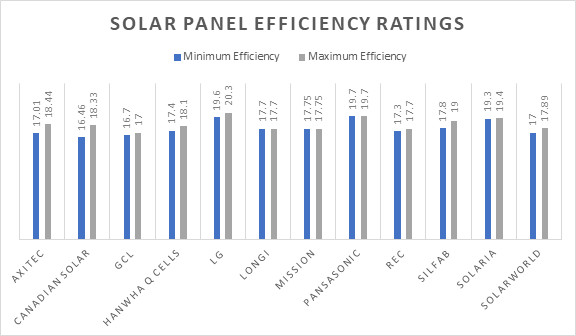
*Efficiency ratings as of June 2018
Solar panel efficiency ratings are another important indicator of a modules overall quality and capabilities. Average efficiency ratings range between 15 to 20 percent, with the manufacturers LG Solar, Panasonic and Solaria currently holding the highest efficiency ratings of the panels currently available (although Canadian Solar, REC and SolarWorld are still comparable in quality). Though, it is worth noting that the average panel efficiency 5 years ago was 15%, current market expectations are close to 18%-20%+ efficiency ratings. As cell technology continues to grow, it is likely that we will see efficiency ratings increase further.
Silicon Technology
![]()
*Monocrystalline (left), Polycrystalline (right)
Solar cells are primarily made up of silicon. Modules we provide are created using silicon in one of two forms:
Monocrystalline and Polycrystalline. While both of these solar cell types achieve the same desired goal of harvesting and sending a raw form of solar energy towards your inverter system, they are created different and have a few differences between the two.
Monocrystalline solar cells consist of "single-crystalline silicon", they are commonly black in color and are known to be of slightly higher quality and cost to produce than their polycrystalline counterpart. Notably, mono silicon cells tend to have higher efficiency ratings than poly silicon cells, as they are made up of a higher quality silicon. Due to these better efficiency ratings, they require less space to fulfill energy wattage needs, and are more common in larger watt modules. Most importantly though is their ability to live longer through higher reliability, thus securing the solar panels long term investment run.
Polycrystalline solar cells consist of raw silicon melted into a multi-crystalline silicon mold, which is then formed into a solar cell. Poly solar cells are generally blue in color and are known to be less expensive to manufacture. They do have a lower heat tolerance, and efficiency is known to be lower. Due to the less efficiency of poly solar cells, the modules they inhabit are generally of lesser wattage, and therefore, PV arrays need more of these modules to achieve the desired system parameters.
Ambient Temperature Range
Temperature ranges of modules are typically between -20°C to +85°C, which cover installations in the majority of the United States. Installers who live under more extreme weather conditions such as those in Alaska, and Arizona should be aware of the temperature ranges of solar panels. Panels that operate outside of their operating range will be less efficient overall. Proper maintenance and the use of optimizers or microinverters can assist in regulating and enhancing your panels under consistent extreme temperature.
Conclusion
In conclusion, although many of the panels in the solar market are comparable, it is important to keep your geographic limitations in mind. Further, understanding the efficiency rating of your module will make it easy to monitor your system and ensure it is working at its maximum efficiency. This will lead to a better energy yield for your solar power system and a higher ROI period for your wallet.